Description of the disease, what are its dangers
Types and complications of thoracic osteochondrosis
- Back pain, characterized by acute, sharp pain in the form of low back pain, located in the thoracic spine. This condition is accompanied by muscle tightness, neck and chest movement problems;
- Backache, pain slowly getting worse. Breathing in and turning the body, as well as staying in one position for long periods of time, can increase discomfort. At night, the discomfort deepens and disappears while walking.
- Digestive system diseases;
- persistent pain;
- interruption of cardiac activity;
- Decreased ability to conceive;
- Pulmonary dysfunction caused by connective tissue proliferation.
Why do thoracic spine lesions occur?
- harm and damage;
- The sector is overburdened, including in childhood;
- Age-related changes are associated with decreased nutrition of the disc tissue between the vertebrae;
- Endocrine disorders, especially menopause;
- Age-related calcium malabsorption;
- being overweight;
- Vascular problems, atherosclerotic deposits in blood vessels in the chest;
- Weak muscle corset.
How does the pathology manifest?
- Discomfort in the heart area, reminiscent of angina;
- Pain and shortness of breath when breathing, also manifesting as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and obstructive pulmonary disease;
- Pain in the upper abdomen below the ribs, similar to symptoms of gastrointestinal disease.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
- Meant to eliminate the source of spinal inflammation;
- Medications that reduce muscle tone and the risk of compression of the sensory roots of the spinal cord;
- Neuroprotective agent designed to help restore nerve fibers.
Osteochondrosis of the chest
Why is thoracic osteochondrosis called a "chameleon"?
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Radical symptoms
- Reduced or lost responses;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- muscle weakness;
- Radix pain.
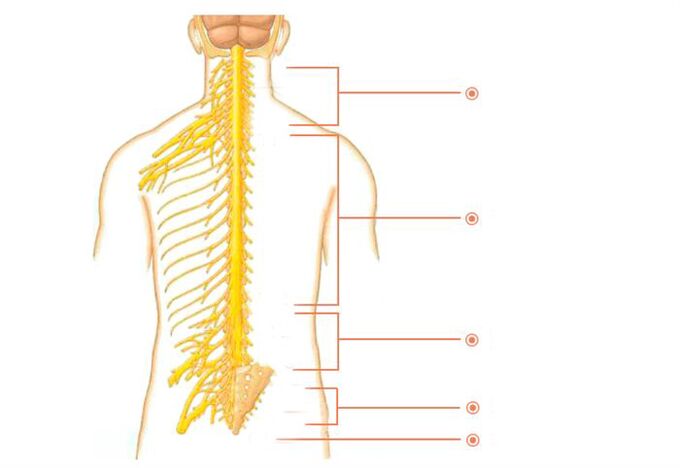
innervation area of thoracic segment
reflex symptoms
- Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis depend on the stage of osteochondrosis.
- The condition gets worse when bending over or trying to stand up.
- Symptoms usually appear after the age of 35-45 years.
- The incidence of these disorders is approximately 3 times higher in women than in men.
stage of disease
| stage | Variety | symptom |
| first | The disc becomes dehydrated, causing a loss of elasticity. Their height decreases, but their width increases—the discs gradually flatten. | The pain occurs directly over the damaged ring. It can be pulled or shot. |
| second | The annulus fibrosus begins to disintegrate. The nerve roots are compressed, causing pain. | Pain when moving. Discomfort occurs when you remain in one position for an extended period of time. |
| third | The annulus fibrosus ruptures, causing a herniated disc. Scoliosis or pathological kyphosis occurs. | Pain when moving. Discomfort occurs when you remain in one position for an extended period of time. |
| fourth | Friction occurs between the vertebrae, causing the intervertebral joints to shift. Inflammation of the tissue surrounding the vertebrae. Cartilage tissue is replaced by bone tissue, reducing motor function. Fibrosis occurs. | Pain when moving. Discomfort occurs when you remain in one position for an extended period of time. |
disease extent
| degree | changes and symptoms |
| first | Disc rupture caused by sudden movement or excessive force. Severe pain, similar to an electric current running down the spine. Muscle strain. |
| second | It is characterized by spinal instability. Pain when moving. protrude. |
| third | The pain becomes constant. Loss of feeling. Gait changes. Severe headache. Difficulty breathing. Tachycardia. |
| fourth | Spinal instability: The vertebrae slip and twist. Osteophytes grow, squeezing spinal nerves and putting pressure on the spinal cord. |
Diagnosis is key to correct treatment
Who to contact and how to get tested for osteochondrosis
treat
- Eliminate pain syndrome;
- Eliminate damaged function at the roots of the spinal cord;
- Preventing the progression of degenerative dystrophic changes in spinal structures.
What methods are considered primary treatments?
physiotherapy
Magnetic laser, magnetic therapy, novocaine SMT, hydrocortisone ultrasound, etc.
Sports therapy and massage
How does gentle manual therapy work?
- The load on the affected vertebrae and discs will be relieved and distributed correctly;
- Relaxes muscles and helps them return to normal;
- Relieving the patient from clamping;
- Improve disk power supply;
- Will restore the body’s motor functions;
- Normalizes blood circulation.
acupuncture
Treatment of female pathologies
What should I do if my condition gets worse?
prevention
- weight adjustment;
- Cycling, running, swimming, yoga and other sports;
- Daily walks;
- Take vitamin complexes and cartilage protectants;
- Reduce back pressure;
- Prompt treatment of musculoskeletal disorders.